| Augmented Language |
|
|
|
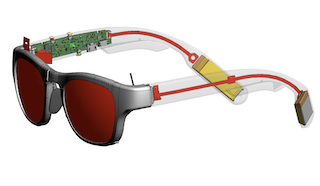
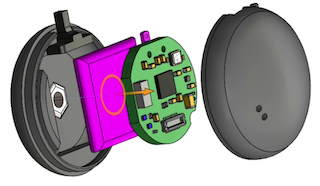
| Wearable Subtitles facilitates communication for deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals through real-time speech-to-text in the user's line of sight in a proof-of-concept eyewear display. The hybrid, low-power wireless architecture is designed for all-day use with up to 15 hours of continuous operation. |
Wearable Subtitles: Augmenting Spoken Communication with Lightweight Eyewear for All-day Captioning
Olwal, A., Balke, K., Votintcev, D., Starner, T., Conn, P., Chinh, B., and Corda, B.
Proceedings of UIST 2020 - Best Demo Honorable Mention Award (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Virtual Event, Oct 20-23, 2020, pp. 1108-1120.
UIST 2020 - Best Demo Honorable Mention Award
|
![PDF [16MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
Visual Captions fine-tuned large language model suggests relevant real-time visuals during vieoconferencing meetings. We open-sourced the work in our ARChat ChromePlugin.
Our work on text stability proposes new metrics and techniques that significantly reduce viewer disrtaction and fatique, while increasing reading comfort.
Google ARChat on Github -> |
Visual Captions: Augmenting Verbal Communication with On-the-fly Visuals
Liu, X, Kirilyuk, V., Yuan, X, Olwal, A., Chi, P., Chen, X., and Du, R.
Proceedings of CHI 2023 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Hamburg, Germany, Apr 23-28, 2023, pp. 1-20.
CHI 2023
|
![PDF [30MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
Modeling and Improving Text Stability in Live Captions
Liu, B., Zhang, J., Ferrer, L., Xu, S., Bahirwani, V., Smus, B., Olwal, A., and Du, R.
CHI 2023 Extended Abstracts (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Hamburg, Germany, Apr 23-28, 2023, pp. 1-9.
CHI 2023
|
![PDF [3MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
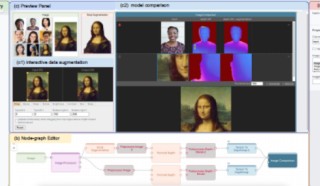
Visual Blocks for ML, formerly called Rapsai, provides a no-code graph building experience through its visual editor. Users can create and connect different components (nodes) to rapidly build an ML pipeline, and see the results in real-time. This work enables better model evaluation through interactive performance characterization, data augmentation and visual comparisons.
Google AI Blog: Visual Blocks ->
visualblocks.withgoogle.com -> |
Rapsai: Accelerating Machine Learning Prototyping of Multimedia Applications through Visual Programming
Du, R., Li, N., Jin, J., Carney, M., Miles, S., Kleiner, M., Yuan, X., Zhang, Y., Kulkarni, A., Liu, X., Sabie, A., Orts-Escolano, S., Kar, A., Yu, P., Iyengar, R., Kowdle, A., and Olwal, A.
Proceedings of CHI 2023 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Hamburg, Germany, Apr 23-28, 2023, pp. 1-23.
CHI 2023
|
![PDF [9MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
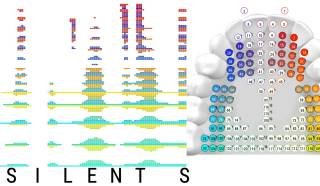
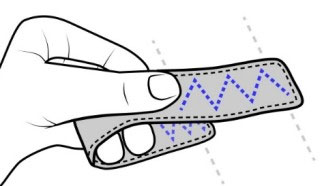
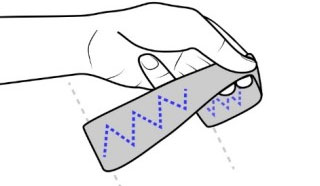
| SilentSpeller enables mobile silent texting using a dental retainer with capacitive touch sensors to track tongue movement. Users type by spelling words without voicing. Comparing silent spelling to current practice suggests that SilentSpeller may be a viable alternative for silent mobile text entry. |
SilentSpeller: Towards mobile, hands-free, silent speech text entry using electropalatography
Kimura, N., Gemicioglu, T., Womack, J., Zhao, Y., Li, R., Bedri, A., Su, Z., Olwal, A., Rekimoto, J., and Starner
Proceedings of CHI 2022 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), New Orleans, LA, Apr 19-May 5, 2022, pp. 1-19, Article 288.
CHI 2022
|
![PDF [23MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
Mobile, Hands-free, Silent Speech Texting Using SilentSpeller
Kimura, N., Gemicioglu, T., Womack, J., Li, R., Zhao, Y., Bedri, A., Olwal, A., Rekimoto, J., and Starner, T.
CHI 2021 Extended Abstracts (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Virtual Event, May 8-13, 2021, pp. 1-5, Article 178.
CHI 2021
|
![PDF [16MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| ProtoSound allows customizing sound recognition models by recording a few examples, thereby enabling personalized and fine-grained categories. Results show that ProtoSound personalized the model on-device in real-time and accurately learned sounds across diverse acoustic contexts. |
ProtoSound: A Personalized and Scalable Sound Recognition System for Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Users
Jain, D., Nguyen, K. H. A., Goodman, S., Grossman-Kahn, R., Ngo, H., Kusupati, A., Du, R., Olwal, A., Findlater, L., and Froehlich, J.E.
Proceedings of CHI 2022 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), New Orleans, LA, Apr 29-May 5, 2022, pp. 1-16, Article 305.
CHI 2022
|
![PDF [8MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
| Interactive Textile and Soft Materials |
|
|
|
Hidden Interfaces leverages a technique for ultrabright graphics that can pass through transmissive materials, allowing interfaces to blend into traditional aesthetics by providing on-demand interaction through wood, textile, plastic and mirrored surfaces.
Google AI Blog: Hidden Interfaces -> |
|
|
|
|
E-Textile Microinteractions leverage the I/O Braid architecture for soft electronics to combine continuous twist sensing with casual, discrete gestures, such as flicks, slides, pinches, grabs and pats.
Google AI Blog: E-Textile Microinteractions -> |
E-Textile Microinteractions: Augmenting Twist with Flick, Slide and Grasp Gestures for Soft Electronics
Olwal, A., Starner, T., and Mainini, G.
Proceedings of CHI 2020 (ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Honolulu, HI, Apr 25-30, 2020, pp. 1-13.
CHI 2020
|
![PDF [19MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| I/O Braid is an interactive textile cord with embedded sensing and visuals. It senses user's proximity, touch, and twist, while embedded fiber optics enable spiraling light feedback. |
I/O Braid: Scalable Touch-Sensitive Lighted Cords Using Spiraling, Repeating Sensing Textiles and Fiber Optics
Olwal, A., Moeller, J., Priest-Dorman, G., Starner, T., and Carroll, B.
Proceedings of UIST 2018 - Best Demo Award (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Berlin, Germany, Oct 14-17, 2018, pp. 485-497.
UIST 2018 - Best Demo Award
|
![PDF [18MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| SensorSnaps are low-power wireless sensor nodes that seamlessly integrate into caps of fabric snap fasteners. SensorSnaps provide a new technique to quickly and intuitively augment any location on the clothing with sensing capabilities. |
SensorSnaps: Integrating Wireless Sensor Nodes into Fabric Snap Fasteners for Textile Interfaces
Dementyev, A., Galvez, T., and Olwal, A.
Proceedings of UIST 2019 (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), New Orleans, LA, Oct 20-23, 2019, pp. 17-28.
UIST 2019
|
![PDF [4MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
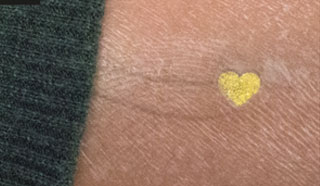
| SkinMarks are thin and conformal skin electronics for on-body interaction. They enable precisely localized input and visual output on strongly curved and elastic body landmarks. |
SkinMarks: Enabling Interactions on Body Landmarks Using Conformal Skin Electronics
Weigel, M., Nittala, A., Olwal, A., and Steimle, J.
Proceedings of CHI 2017 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Denver, CO, May 6-11, 2017, pp. 3095-3105.
CHI 2017
|
![PDF [2MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
On-Skin Interaction Using Body Landmarks
Steimle, J., Bergstrom-Lehtovirta, J., Weigel, M., Nittala, A.S., Boring, S., Olwal, A., Hornbæk, K.
Computer 2017 (IEEE Computer, Cover Feature, Vol. 50, no 10), Oct, 2017, pp. 19-27.
Computer 2017
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
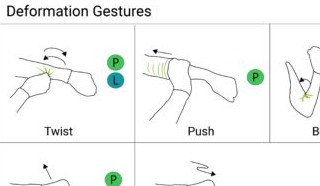
| SmartSleeve is a deformable textile sensor for surface and deformation gestures. It enables new interaction techniques using a hybrid gesture detection pipeline. |
SmartSleeve: Real-time Sensing of Surface and Deformation Gestures on Flexible, Interactive Textiles, using a Hybrid Gesture Detection Pipeline
Parzer, P., Sharma, A., Vogl, A., Steimle, J., Olwal, A., Haller, M.
Proceedings of UIST 2017 (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Quebec City, ON, Oct 22-25, 2017, pp. 565-577.
UIST 2017
|
![PDF [1.2MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| StretchEBand is a stitch-based stretch sensor, which can be rapidly fabricated for integration into soft electronics for wearables, mobile devices, clothing, furniture, and toys. |
StretchEBand: Enabling fabric-based interactions through Rapid Fabrication of Textile Stretch Sensors
Vogl, A., Parzer, P., Babic, T., Leong, J., Olwal, A., and Haller, M.
Proceedings of CHI 2017 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Denver, CO, May 6-11, 2017, pp. 2617-2627.
CHI 2017
|
![PDF [15MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
proCover uses pressure-sensing textiles to offer non-invasive, self-applicable and customizable sensory augmentation for prosthetics.
FlexTiles are flexible, stretchable pressure-sensitive tactile input sensors for covering large areas, 3D objects, and deformable underlying shapes. |
proCover: Sensory Augmentation of Prosthetic Limbs Using Smart Textile Covers
Leong, J. Parzer, P., Perteneder, F., Babic, T., Rendl, C., Vogl, A., Egger, H., Olwal, A., and Haller, M.
Proceedings of UIST 2016 - Best Paper Award (Top 1%) (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Tokyo, Japan, Oct 16-19, 2016, pp. 335-346.
UIST 2016 - Best Paper Award (Top 1%)
|
![PDF [2MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
FlexTiles: A Flexible, Stretchable, Formable, Pressure Sensitive, Tactile Input Sensor
Parzer, P., Probst, K., Babic, T., Rendl, C., Vogl, A., Olwal, A., and Haller, M.
CHI 2016 Extended Abstracts (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), San Jose, CA, May 7-12, 2016, pp. 3754-3757.
CHI 2016
|
![PDF [0.7MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
| Embedded Sensing |
|
|
|
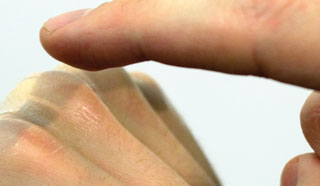
Haptics with Input introduces new opportunities for the Linear Resonant Actuator (LRA), which is ubiquitous in wearable and mobile devices. Through active and passive back-EMF sensing, it could enable new touch and pressure sensing, and allow mobile devices to sense which surfaces they are placed on.
Google AI Blog: Haptics with Input -> |
Haptics with Input: Back-EMF in Linear Resonant Actuators to Enable Touch, Pressure and Environmental Awareness
Dementyev, A., Olwal, A., and Lyon, R.F.
Proceedings of UIST 2020 (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Virtual Event, Oct 20-23, 2020, pp. 420-429.
UIST 2020
|
![PDF [3MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| Zensei is an implicit sensing system that leverages bio-sensing, signal processing and machine learning to classify uninstrumented users by their body's electrical properties. |
Zensei: Embedded, Multi-electrode Bioimpedance Sensing for Implicit, Ubiquitous User Recognition
Sato, M., Puri, R., Olwal, A., Ushigome, Y., Franciszkiewicz, L., Chandra, D., Poupyrev, I., and Raskar, R.
Proceedings of CHI 2017 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Denver, CO, May 6-11, 2017, pp. 3972-3985.
CHI 2017
|
![PDF [15MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
Zensei: Augmenting Objects with Effortless User Recognition Capabilities through Bioimpedance Sensing
Sato, M., Puri, R., Olwal, A., Chandra, D., Poupyrev, I., and Raskar, R.
UIST 2015 Extended Abstracts (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Charlotte, NC, Nov 8-11, 2015, pp. 41-42.
UIST 2015
|
![PDF [0.7MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| SpecTrans uses laser and multi-directional, multispectral illumination to classify exotic materials such as glass, transparent plastic, and metal. |
SpecTrans: Versatile Material Classification for Interaction with Textureless, Specular and Transparent Surfaces
Sato, M., Yoshida, S., Olwal, A., Shi, B., Hiyama, A., Tanikawa, T., Hirose, M., Raskar, R.
Proceedings of CHI 2015 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Seoul, South Korea, Apr 18-23, 2015, pp. 2191-2200.
CHI 2015
|
![PDF [21MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| SpeckleSense exploits laser speckle sensing for precise, high-speed, low-latency motion tracking, which can be applied to a wide range of interaction scenarios and devices. |
SpeckleEye: Gestural Interaction for Embedded Electronics in Ubiquitous Computing
Olwal, A., Bardagjy, A., Zizka, J., and Raskar, R.
CHI 2012 Extended Abstracts (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Austin, TX, May 5-10, 2012, pp. 2237-2242.
CHI 2012
|
![PDF [8MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
SpeckleSense: Fast, Precise, Low-cost and Compact Motion Sensing using Laser Speckle
Zizka, J., Olwal, A., and Raskar, R.
Proceedings of UIST 2011 (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Santa Barbara, CA, Oct 16-19, 2011, pp. 489-498.
UIST 2011
|
![PDF [4.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
| Grabity |
|
|
|
Grabity is a wearable haptic device that simulates kinesthetic pad opposition grip forces and weight for grasping virtual objects in VR. Mounted on index finger and thumb, it enables precision grasps with a wide range of motion.
Reconfigurable Tactile Elements are micro-robots that can be repositioned around a mobile device's edge for dynamic physical controls and haptic feedback. shiftIO implements this by utilizing magnetic locomotion through flexible PCB coils or bi-stable magnets. |
Grabity: A Wearable Haptic Interface for Simulating Weight and Grasping in Virtual Reality
Choi, I., Culbertson, H., M.R., Olwal, A., and Follmer, S.
Proceedings of UIST 2017 - Best Paper Award (Top 1%) (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Quebec City, ON, Oct 22-25, 2017, pp. 119-130.
UIST 2017 - Best Paper Award (Top 1%)
|
![PDF [2.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
shiftIO: Reconfigurable Tactile Elements for Dynamic Affordances and Mobile Interaction
Strasnick, E., Yang, J., Tanner, K., Olwal, A., and Follmer, S.
Proceedings of CHI 2017 - Best Paper Honorable Mention Award (Top 5%) (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Denver, CO, May 6-11, 2017, pp. 5075-5086.
CHI 2017 - Best Paper Honorable Mention Award (Top 5%)
|
![PDF [0.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| Physical Telepresence uses shape capture and display to enhance interactions with remote people and environments. |
Physical Telepresence: Shape Capture and Display for Embodied, Computer-mediated Remote Collaboration
Leithinger, D., Follmer, S., Olwal, A., and Ishii, H.
Proceedings of UIST 2014 (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Honolulu, HI, Oct 5-8, 2014, pp. 461-470.
UIST 2014
|
![PDF [5.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
Shape Displays: Spatial Interaction with Dynamic Physical Form
Leithinger, D., Follmer, S., Olwal, A., and Ishii, H.
CG&A 2015 (IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, Vol. 35, no 5), Sep-Oct, 2015, pp. 417-426.
CG&A 2015
|
![PDF [0.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
inFORM dynamically changes material and form to adapt the physical and virtual interface.
Sublimate explores rapid and fluid transitions between physical and visual representations of dynamic digital content. |
inFORM: Dynamic Physical Affordances and Constraints through Shape and Object Actuation
Follmer, S., Leithinger, D., Olwal, A., Hogge, A., and Ishii, H.
Proceedings of UIST 2013 (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), St Andrews, UK, Oct 8-11, 2013, pp. 417-426.
UIST 2013
|
![PDF [0.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
Sublimate: State-Changing Virtual and Physical Rendering to Augment Interaction with Shape Displays
Leithinger, D., Follmer, S., Olwal, A., Luescher, S., Hogge, A., Lee, J., and Ishii, H.
Proceedings of CHI 2013 - Best Paper Honorable Mention Award (Top 5%) (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Paris, France, Apr 27-May 2, 2013, pp. 1441-1450.
CHI 2013 - Best Paper Honorable Mention Award (Top 5%)
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| Jamming User Interfaces enable programmable stiffness, haptic feedback and deformation, for new types of flexible and shape-changing interactions. |
Jamming User Interfaces: Programmable Particle Stiffness and Sensing for Malleable and Shape-Changing Devices
Follmer, S., Leithinger, D., Olwal, A., Cheng, N., and Ishii, H.
Proceedings of UIST 2012 - Best Paper Award (Top 1%) (ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology), Cambridge, MA, Oct 7-10, 2012, pp. 519-528.
UIST 2012 - Best Paper Award (Top 1%)
|
![PDF [8.3MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
| Spatial Displays and Augmented Reality |
|
|
|
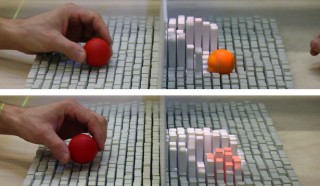
| Our immaterial display generates pixels that float in mid-air. The surface enables new interaction possibilities as users can reach, walk and talk through the display. |
An Immaterial Pseudo-3D Display with 3D Interaction
DiVerdi, S., Olwal, A., Rakkolainen, I., and Höllerer, T.
3D TV Book (Three-Dimensional Television: Capture, Transmission, and Display), Springer, Heidelberg, 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-72531-2.
3D TV Book
|
![PDF [2.5MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
Consigalo: Multi-user, Face-to-face Interaction on an Immaterial Display
Olwal, A., DiVerdi, S., Rakkolainen, I., and Höllerer, T.
Proceedings of INTETAIN 2008 (2nd International Conference on Intelligent Technologies for Interactive Entertainment), Cancun, Mexico, Jan 8-10, 2008.
INTETAIN 2008
|
![PDF [1.8MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
An Immaterial, Dual-sided Display System with 3D Interaction
Olwal, A., DiVerdi, S., Candussi, N., Rakkolainen, I., and Höllerer, T.
Proceedings of IEEE VR 2006 (IEEE Virtual Reality Conference 2006), Alexandria, VA, Mar 25-29, 2006, pp. 279-280.
IEEE VR 2006
|
![PDF [2.3MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
A Novel Walk-through 3D Display
DiVerdi, S., Rakkolainen, I., Höllerer, T., and Olwal, A.
Proceedings of SPIE 2006 Electronic Imaging (Vol. 6055, Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems XIII), San Jose, CA, Jan 15-18, 2006, pp. 428-437.
SPIE 2006 Electronic Imaging
|
![PDF [1.6MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
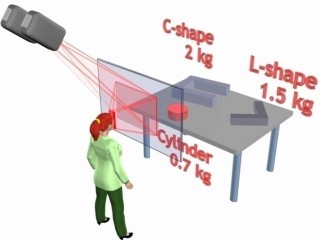
| ASTOR is a transparent 3D window that enhances the space behind it with graphics. It preserves an optically clear view of the real environment, while superimposing dynamic 3D visuals. |
Spatial Augmented Reality on Industrial CNC machines
Olwal, A., Gustafsson, J., and Lindfors, C.
Proceedings of SPIE 2008 Electronic Imaging (Vol. 6804, The Engineering Reality of Virtual Reality 2008), San Jose, California, Jan 27-31, 2008.
SPIE 2008 Electronic Imaging
|
![PDF [3.9MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
ASTOR: An Autostereoscopic Optical See-through Augmented Reality System
Olwal, A., Lindfors, C., Gustafsson, J., Kjellberg, T., and Mattson, L.
Proceedings of ISMAR 2005 (IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality), Vienna, Austria, Oct 5-8, 2005, pp. 24-27.
ISMAR 2005
|
![PDF [3.3MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| SpaceTop fuses 2D and 3D interactions in a desktop workspace. It simultaneously allows users to type, click, draw in 2D, and directly manipulate interface elements that float in the 3D space. |
SpaceTop: Integrating 2D and Spatial 3D Interactions in a See-through Desktop
Lee, J., Olwal, A., Ishii, H., and Boulanger, C.
Proceedings of CHI 2013 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Paris, France, Apr 27-May 2, 2013, pp. 189-192.
CHI 2013
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
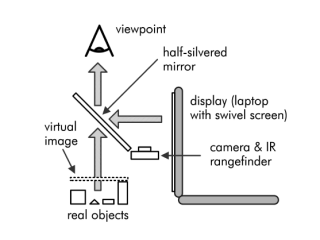
| POLAR is a lightweight mobile workspace for augmented reality. Using a foldable, optical see-through setup and hybrid user tracking, it enables annotated views of small physical objects without the need for worn technology. |
POLAR: Portable, Optical see-through, Low-cost Augmented Reality
Olwal, A., and Höllerer, T.
Proceedings of VRST 2005 (ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality and Software Technology), Monterey, CA, Nov 7-9, 2005, pp. 227-230.
VRST 2005
|
![PDF [1.1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
| Interaction Techniques for Medical Imaging and Diagnostics |
|
|
|
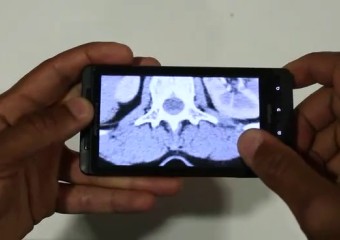
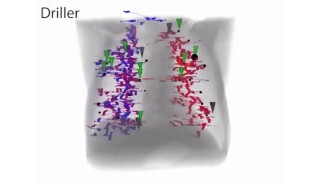
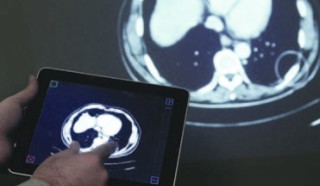
| We collect gaze data from radiologists that search 3D CT scans for lung nodules. Analysis and interactive 3D visualisations of eye tracking data indicate 2 dominant search strategies, where "Drilling" is superior over "Scanning". |
Scanners and Drillers: Characterizing Expert Visual Search through Volumetric Images
Drew, T., Vo, M., Olwal, A., Jacobson, F., Seltzer, S., and Wolfe, J.
JOV 2013 (Journal of Vision, Vol. 13, no 10.), Aug 6, 2013.
JOV 2013
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| Our multi-display groupware system for medical team meetings synchronizes multi-touch and pen interaction across various mobile and stationary displays. |
Design and Evaluation of Interaction Technology for Medical Team Meetings
Olwal, A., Frykholm, O., Groth, K., and Moll, J.
Proceedings of INTERACT 2011 (IFIP TC13 Conference on Human-Computer Interaction), Lisbon, Portugal, Sep 5-9, 2011, pp. 505-522.
INTERACT 2011
|
![PDF [3.4MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
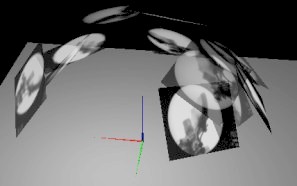
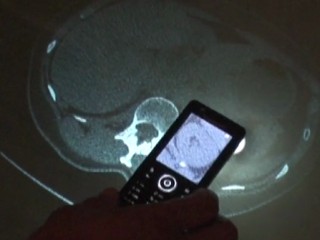
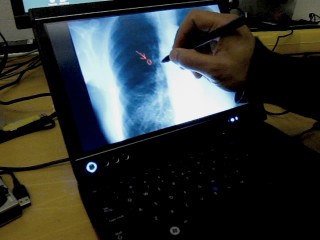
| Our system tracks and augments 2D X-ray images in image-guided surgery. It provides interactive spatiotemporal visualizations of 2D X-rays in timeline views and 3D clouds. |
3D Visualization and Interaction with Spatiotemporal X-ray Data to Minimize Radiation in Image-guided Surgery
Ioakeimidou, F., Olwal, A., Nordberg, A., and von Holst, H.
Proceedings of CBMS 2011 (International Symposium on Computer-based Medical Systems), Bristol, UK, Jun 27-30, 2011.
CBMS 2011
|
![PDF [1.1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
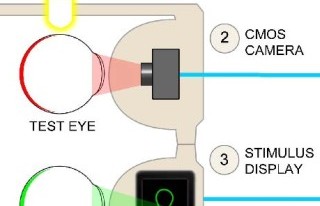
| Our interactive device images and visualizes the retina. Its use of indirect diffuse illumination and binocular coupling, avoids the complexity of traditional devices. |
Computational Retinal Imaging via Binocular Coupling and Indirect Illumination
Lawson, E., Boggess, J., Khullar, S., Olwal, A., Wetzstein, G., and Raskar, R.
SIGGRAPH 2012 Talks (International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques), Los Angeles, CA, Aug 5-9, 2012.
SIGGRAPH 2012
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
| Mobile Augmented Reality |
|
|
|
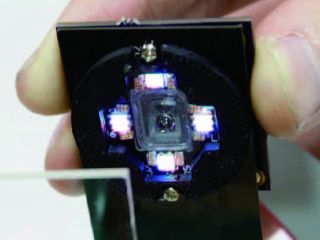
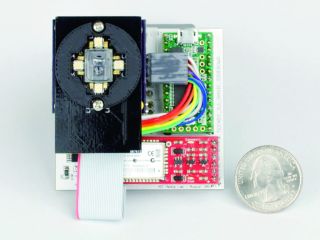
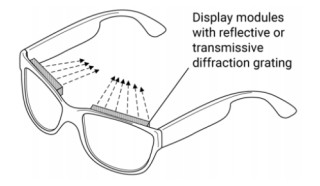
| 1D Eyewear embed arrays of LEDs and holographic symbols in glasses frames. Computer-generated holograms (CGHs) allow transmissive, reflective or steerable display configurations for high-resolution symbols in normal-looking head-worn displays. |
|
|
|
|
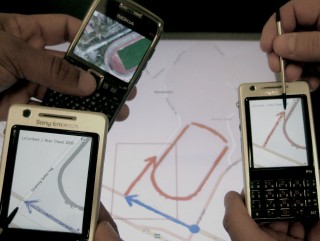
| WatchThru augments smartwatches with a transparent display to enable wrist-worn interaction techniques, such as Pop-up Visuals, Second Perspective and Peek-through AR. |
WatchThru: Expanding Smartwatch Displays with Mid-air Visuals and Wrist-worn Augmented Reality
Wenig, D., Schöning, J., Olwal, A., Oben, M., and Malaka, R.
Proceedings of CHI 2017 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Denver, CO, May 6-11, 2017, pp. 716-721.
CHI 2017
|
![PDF [1.1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| LUMAR combines 2D and 3D interaction with a static display, and enables a 3-layered information space, where the mobile phone provides an augmented reality viewport into the real world. |
|
|
|
|
| This framework explores tangible interaction for handheld AR. Hardware-accelerated rendering of illumination and shadows enables real-time interaction with realistic models, through spatial motion or touch screen manipulation. |
|
|
| Spatially-Aware and Tangible Devices |
|
|
|
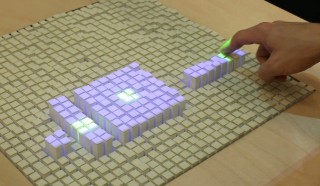
| SurfaceFusion senses tangible, physical objects on interactive surfaces. It introduces a hybrid technique that combines RFID and computer vision, to avoid the need for visual markers. |
|
|
|
|
| T(ether) introduces gestural techniques that exploit proprioception to adapt the interface of a handheld Virtual Reality viewport, based on the hand's position above, behind or on its surface. |
T(ether): Spatially-Aware Handhelds, Gestures and Proprioception for Multi-User 3D Modeling and Animation
Lakatos, D., Blackshaw, M., Olwal, A., Barryte, Z., Perlin, K., and Ishii, H.
Proceedings of SUI 2014 (ACM Symposium on Spatial User Interaction), Honolulu, HI, Oct 4-5, 2014, pp. 90-93.
SUI 2014
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| We synchronize mobile devices with interaction on the large touch surface to expand expressiveness. The mobile displays provide denser resolution, while the controls enable better precision and physical affordances. |
|
|
|
|
| LightSense tracks mobile devices on static or dynamic displays, to enable context-sensitive visuals and interaction, based on spatial motion and position. |
|
|
| Interaction Techniques and Devices |
|
|
|
| Hybrid Watch User Interfaces leverage electro-mechanical hands and a dynamic watch dial to enable computation and connectivity while preserving the aesthetics of traditional analog watches. |
|
|
|
|
| Rubbing and Tapping are fast and precise interaction techniques for single-touch, multi-touch and pen-based devices. They leverage minimal gestures for quick zoom and pan actions. |
Rubbing and Tapping for Precise and Rapid Selection on Touch-Screen Displays
Olwal, A., Feiner, S., and Heyman, S.
Proceedings of CHI 2008 - Best Paper Honorable Mention Award (Top 5%) (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Florence, Italy, Apr 5-10, 2008, pp. 295-304.
CHI 2008 - Best Paper Honorable Mention Award (Top 5%)
|
![PDF [6MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| The OldGen framework addresses accessibility on generic mobile devices by decoupling the software UI from the phone hardware. It makes the UI portable and independent of phone, model or brand. |
OldGen: Mobile Phone Personalization for Older Adults
Olwal, A., Lachanas, D., and Zacharouli, E.
Proceedings of CHI 2011 (SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems), Vancouver, BC, May 7-12, 2011, pp. 3393-3396.
CHI 2011
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| Our mobile phantogram viewer enables realistic real-time interaction with 3D models through view-point correct anamorphosis and stereoscopy. |
|
|
| Multimodal Interaction: Pointing, Looking, Gesturing and Speaking |
|
|
|
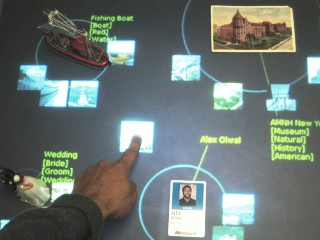
| MAVEN interprets user intention in AR/VR by fusing speech, gesture, viewpoint, pointing direction, and SenseShapes statistics, to improve recognition through multimodal disambiguation. |
SenseShapes: Using Statistical Geometry for Object Selection in a Multimodal Augmented Reality System
Olwal, A., Benko, H., and Feiner, S.
Proceedings of ISMAR 2003 (IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality), Tokyo, Japan, Oct 7-10, 2003, pp. 300-301.
ISMAR 2003
|
![PDF [1.2MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
MAVEN: Mutual Disambiguation of 3D Multimodal Interaction in Augmented and Virtual Reality
Kaiser, E., Olwal, A., McGee, D., Benko, H., Corradini, A., Li, X., Feiner, S., and Cohen, P.
Proceedings of ICMI 2003 (International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces), Vancouver, BC, Nov 5-7, 2003, pp. 12-19.
ICMI 2003
|
![PDF [2.1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| The Flexible Pointer can facilitate selection and interaction with fully or partially obscured objects in 3D environments, and help indicate objects of interest to collaborators in AR/VR. |
|
|
|
|
| Motion guidance for position, direction and continuous velocities, is provided to tracked users using visual, vibrotactile and pneumatic feedback. |
Multimodal Motion Guidance: Techniques for Adaptive Dynamic Feedback
Schönauer, C., Fukushi, K., Olwal, A., Kaufmann, H., and Raskar, R.
Proceedings of ICMI 2012 (ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction), Santa Monica, CA, Oct 22-26, 2012, pp. 133-140.
ICMI 2012
|
![PDF [2MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
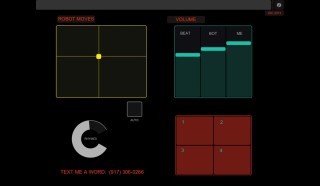
| Cloud Rhymer is a platform that combines cloud technology and robotics. Users can text message a word to the robot, who will start rhyming on that word in sync with the beat. |
Cloud Rhymer: Prototype Demo and Intervention Proposal
Robert, D., Schmitt, P., and Olwal, A.
Proceedings of IDC 2013 (International Conference on Interaction Design and Children), New York, NY, Jun 24-27, 2013, pp. 507-510.
IDC 2013
|
![PDF [2MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
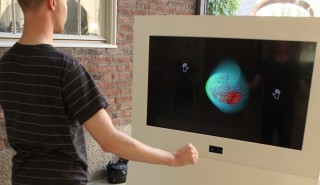
| The HEART project allows the public to experience and interact with a simulation of a beating heart. Blood flow and pressure are visualized in 3D and can be manipulated with gestures using both hands. |
Gestural 3D Interaction with a Beating Heart: Simulation, Visualization and Interaction
Ioakeimidou, F., Ericson, E., Spühler, J., Olwal, A., Forsslund, J., Jansson, J., Sallnäs Pysander, E.-L., and Hoffman, J.
Proceedings of SIGRAD 2011 (Swedish Chapter of Eurographics Conference), Stockholm, Sweden, Nov 17-18, 2011, pp. 93-97.
SIGRAD 2011
|
![PDF [6.3MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
| The Unit framework is a visual dataflow programming language for highly interactive 3D environments. Interaction techniques are abstracted from devices and application, to separate application logic from behavior. |
|
|
|
|
| This mixed reality system allows users to immersively reconfigure data flow in real-time between interaction devices and objects on a running hybrid user interface. |
Immersive Mixed-Reality Configuration of Hybrid User Interfaces
Sandor, C., Olwal, A., Bell, B., and Feiner, S.
Proceedings of ISMAR 2005 (IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality), Vienna, Austria, Oct 5-8, 2005, pp. 110-113.
ISMAR 2005
|
![PDF [1MB]](images/pdf.gif)
|
|
|
|
|
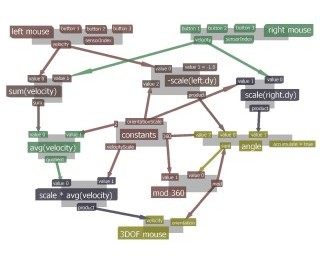
| Prosodic features of speech is used together with audio localization to control interactive applications. This information can also be applied to parameter control, or for disambiguation in speech recognition. |
|
|
| Vision |
|
|
|
Advances in the past century have resulted in unprecedented access to empowering technology, with user interfaces that typically provide clear distinction and separation between environments, technology and people.
The progress in recent decades indicates, however, inevitable developments where sensing, display, actuation and computation will seek to integrate more intimately with matter, humans and machines. This talk will explore some of the radical new challenges and opportunities that these advancements imply for next-generation interfaces. |
|
|
|
|
| The concept of Unobtrusive Augmented Reality is introduced through various systems and techniques that enable sporadic and spontaneous interaction. Unobtrusive AR emphasizes an optically direct view of a visually unaltered physical environment, the avoidance of user-worn technology, and the preference for unencumbering techniques. |
|
|